The name ‘Hangxiety’ is similar to Anxiety, of course they mean almost the same thing. Anxiety can happen at any time, but hangover is experienced after drinking alcohol. It is also commonly known as Booze blues, Beer fear. But they all mean the same thing – they are feelings of shame, guilt or anxiety that can emerge after drinking alcohol. Hangover anxiety or ‘hangxiety’ is not a medical condition.
Many aspects of a hangover, such as dehydration or lack of sleep, add to the feeling of anxiety. Craig Gunn, lecturer and researcher at the School of Psychological Science at the University of Bristol, England, says that excessive amounts of alcohol affect the body’s immune and stress response systems. They say that this increases the level of proinflammatory cytokines and cortisol. In addition, there are also visible effects of a hangover on the body, such as an increased heart rate, which can increase feelings of anxiety in some people.
However, Craig Gunn says that hangover only affects about 12% of drinkers. Why some people have different symptoms from others is not yet clear.
‘Hangxiety’ and the brain
According to an article published in the Journal of Alcohol and Alcoholism in 2019, the mild euphoria we experience after drinking alcohol is due to temporary changes in our chemical messengers, ie neurotransmitters, in the brain. These neurotransmitters affect our mood. At first they create euphoria, but if there is a slight change in their levels, they can suddenly trigger hangover symptoms.
Hangry and dehydration
According to the Cleveland Clinic, excessive thirst is a common symptom of a hangover. Alcohol is diuretic, which means it causes the body to lose fluid faster than normal, making you go to the bathroom more often. After a night of drinking, waking up in the morning may feel more tired and inebriated due to the lack of fluid in the body.
Dehydration can also increase feelings of hangover. A 2014 study published in the journal PLOS One found that people who didn’t drink enough water before drinking alcohol were more likely to experience negative emotions the next day.
Hangover and sleep
Some research suggests that trying to avoid hangover symptoms or hangover by sleeping more is not an effective strategy. According to a review published in Alcohol Journal in 2015, drinking alcohol can disrupt a person’s sleep cycle, while the quality of sleep is also poor. Peaceful sleep is essential for good mental health. In 2016, it has been said in the Sleep Medicine Journal that lack of sleep can increase the level of anxiety of people.
However, Craig Gunn says that the relationship between sleep quality and hangover anxiety is yet to be established.
Hangxiety and Stomach
Hangover can also be associated with an upset stomach. According to a review published in the journal Nutrients in 2021, excessive alcohol consumption alters the composition of the gut microbiome. At the same time, in 2021, it was said in the Clinical Psychology Review Journal that this imbalance in the microbes of the gut may be related to anxiety disorders. However, more research is needed to understand this.
Why does only a few people suffer from hangover?
The ability to drink alcohol varies from person to person. Some do not get intoxicated even after drinking a lot of alcohol, while some start swinging only after drinking a little. According to a report published in the European Neuro psychopharmacology Journal in 2019, people who have a higher alcohol tolerance experience less stress and anxiety the next day.

![Visa and Social Media [TKB World]](https://topknowledgebox.com/iphaphoo/2025/12/15122025.jpg)
![Vishwakarma Puja 2025 [TKB- INDIA]](https://topknowledgebox.com/iphaphoo/2025/09/17092025-150x150.jpg)
![Ganesh Chaturthi 2025[TKB-INDIA]](https://topknowledgebox.com/iphaphoo/2025/08/27082025-150x150.jpg)
![Buddha Purnima 2025 [TKB INDIA]](https://topknowledgebox.com/iphaphoo/2025/05/12052025-150x150.jpg)



More Stories
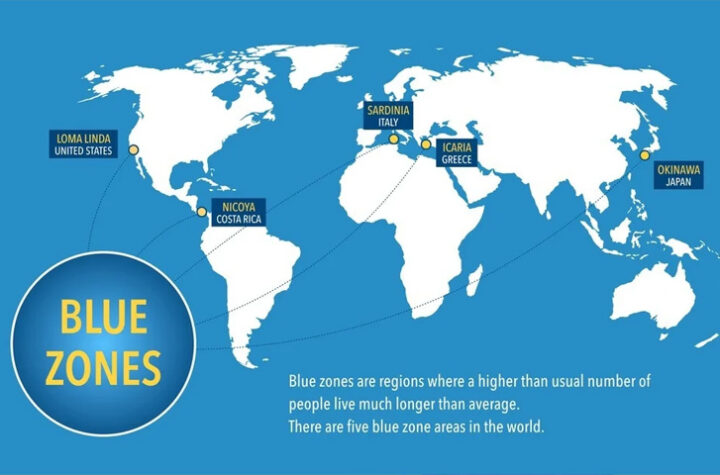
Why do people living in blue zones live longer? 3 reasons that will change your thinking
Essential Oil For Skin[TKB Health]
Chia seeds will give double benefits [TKB Health]